Machimosaurus is a genus of the family Teleosauridae that lived during the Late Jurassic period. Their fossils were found in Morocco, Switzerland. Other fossils have been found in England, France, Germany, and Portugal.
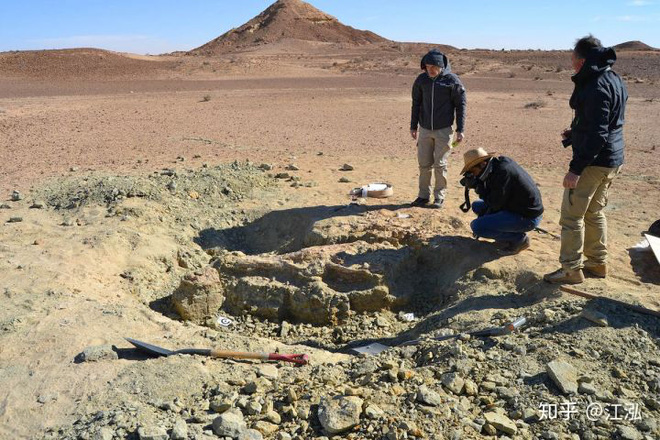

Paleontologists are digging up fossils of Machimosaurus rex.

Fossil skull shape of the giant crocodile Machimosaurus rex.
North Africa in the Mesozoic era was considered the territory of giant animals and included animals with familiar names such as Spinosaurus, white shark Carcharhinus, Carcharodontosaurus, Paralititan, Sarcosuchus.. .
In recent years, a new species of crocodile has been discovered and named King Machimosaurus (Machimosaurus rex). Fossils of this species were found in the Moroccan desert, this fossil specimen is a 1.6 meter long skull and the entire excavation was sponsored by National Geographic.

The team excavated the Machimosaurus rex crocodile fossil.
In early 2016, the research team published a research paper titled “The largest thalattosuchian (Crocodylomorpha) supports teleosaurid survival across the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary” and officially named this giant crocodile Machimosaurus rex.
Judging from the fossils of Machimosaurus rex, paleontologists speculate that this species could have been up to 9.6 meters long and weighed up to nearly 3 tons. From there, it can be seen that Machimosaurus rex is the largest saltwater crocodile ever discovered by humans.
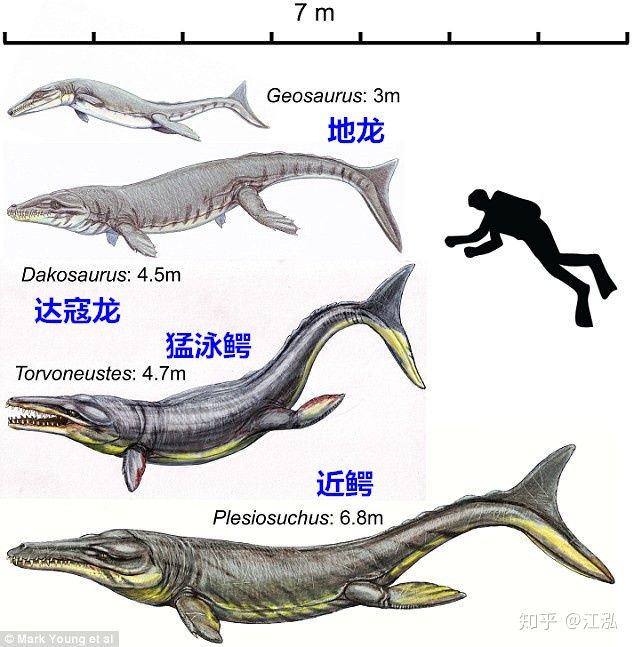
Meanwhile, other saltwater crocodiles that lived during the Mesozoic era were smaller in size, such as Dakosaurus and Metriorhynchus.
But in fact, if you combine both saltwater crocodiles and freshwater crocodiles together, the size of Machimosaurus rex is still smaller than species such as Purussaurus, Sarcosuchus or Deinosuchus.

Machimosaurus rex possessed a long head, but its snout was quite thin and it possessed rows of round, short, and sharp teeth in its mouth. Their noses are grown on the top of their heads, which is an advantageous feature for being able to breathe in the marine environment. In addition, they possess eyes growing on the top of their heads, quite similar to today’s crocodiles.
Through fossil analysis and simulation, paleontologists believe that Machimosaurus rex had a quite slender body but its tail was quite long and wide to support the process of moving under the sea and maintaining sustenance. Maintain body balance.
From there, it can be seen that the Machimosaurus rex evolved to adapt to life in the ocean and could swim at very fast speeds.
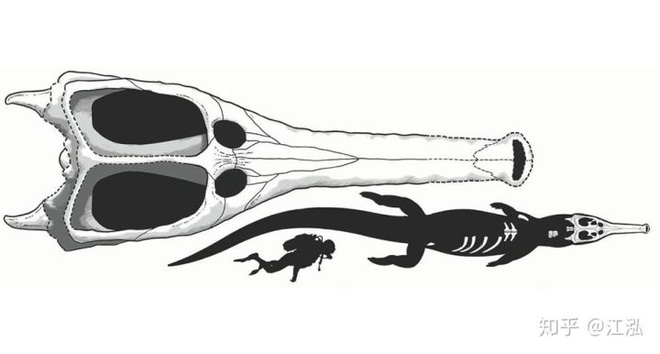
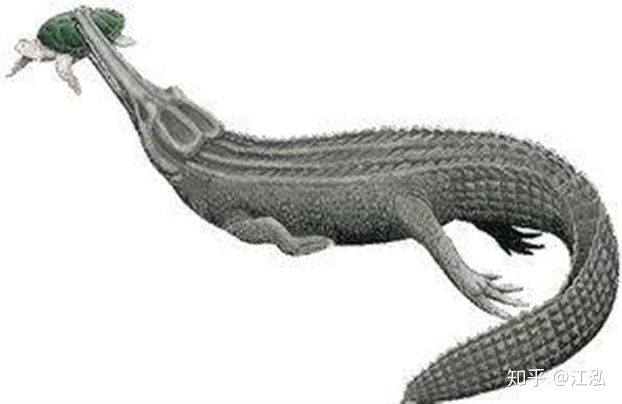
Federico, a paleontologist at the University of Bologna in Italy who participated in the study, said that Machimosaurus’ skull was large, but its teeth were short, thick and round, suggesting that it possessed strong powers. The bite is extremely large and can completely crush a turtle’s shell in just one bite.
Researchers speculate that their main food is fish and dinosaurs, animals near the shore, while other marine animals such as turtles are only considered “desserts”.

.

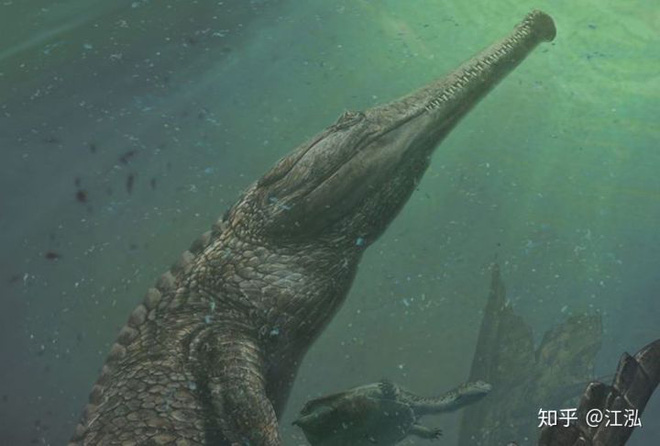
The hunting method of this giant crocodile is quite similar to modern crocodiles, they will lie in ambush for their prey or wait for careless dinosaurs to approach and then carry out an attack. suddenly at high speed and pulled the unlucky animal down to the sea surface.
Bite marks from this giant crocodile have also been found on some fossil specimens of the Cetiosaurus dinosaur found in England. This means that their habitat is not limited to only North Africa like other crocodiles such as Spinosaurus, Carcharodon.

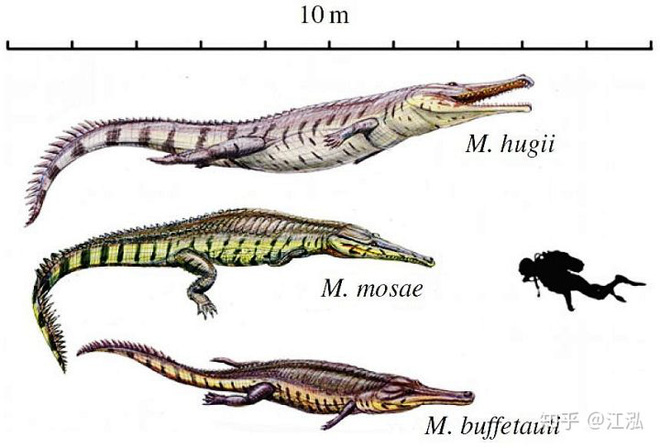
The full name of this giant crocodile is Machimosaurus rex, including the genus name and species name, because Machimosaurus rex is not the only species found in the Machimosaurus genus.
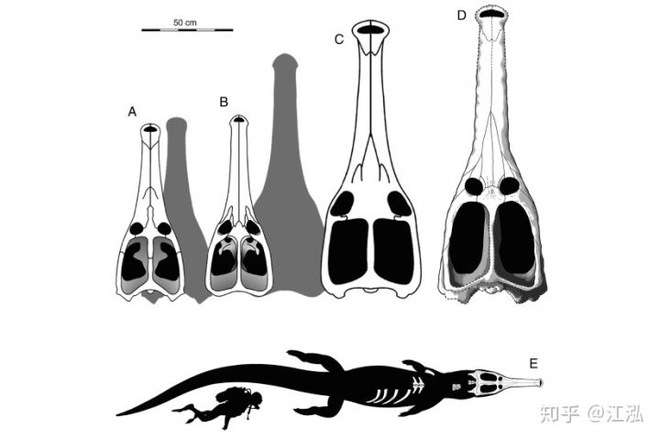
Machimosaurus rex (far right) is the largest species in the genus Machimosaurus.
Fossils of the crocodile genus Machimosaurus were first found in Switzerland in the early 19th century and it was named after the German paleontologist von Schone and it is considered the largest crocodile known during the period. Jurassic period.
There are currently 5 species in the genus Machimosaurus and Machimosaurus rex is the newest and largest species ever discovered. Judging from Machimosaurus fossils, they existed in Switzerland, France, England, Portugal, Germany, Austria, Morocco, and were apparently present throughout prehistoric Europe.
The distribution of Machimosaurus is related to the distribution of land and sea from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Because during that time, the ocean flooded into Europe and North Africa, and obviously this was the habitat of the Machimosaurus crocodile.

.
The discovery of Machimosaurus rex not only renewed the size limit of marine crocodiles in the Mesozoic period but also extended the survival limit of Machimosaurus species to the Cretaceous period, from 130 million to 120 million years ago.
Previously, there was a view that there was an extinction event at the end of the Jurassic period that caused a group of crocodile-like animals called teleosaurids to become extinct during this extinction. But the discovery of Machimosaurus rex reveals that if a mass extinction ever took place, it would not kill off life across the planet.
“The new discovery provides further evidence that many marine reptiles crossed borders and survived extinction,” concluded Brusatte – a paleontologist at the University of Edinburgh, UK.